 |
Chinese scientists published a paper in the journal Nature Nanotechnology that they had made a breakthrough in the preparation of monocrystalline graphene. Through the adjustment and improvement of chemical vapor deposition (CVD), they have increased the production speed of graphene films by 150 times. New research lays the foundation for the large-scale application of graphene.
Graphene is a two-dimensional crystal material composed of carbon atoms and has only one atom of thickness. Its excellent properties in electricity, light and mechanical strength make it a potential application in electronics, solar cells, and sensors. Although the demand is huge, its preparation speed is slow, and the utilization rate has been hovering around 25%, which has become one of the bottlenecks restricting its entry into practical applications. At present, a method for preparing high-quality graphene is mainly a chemical vapor deposition method except a tape peeling method, silicon carbide, or a metal surface epitaxial growth method. However, it still takes a long time to produce monocrystalline graphene film by CVD technology. It takes at least one day to prepare a cm square monocrystalline graphene film, which is very slow.
In the new study, researchers at Peking University and Hong Kong Polytechnic University in China developed a new technology that can accelerate this process from 0.4 micron per second to 60 micron per second, a 150-fold increase in speed. One of the tricks is to add a little oxygen directly to the copper foil involved in the reaction.
According to the researchers, the oxide substrate releases oxygen at high temperatures of up to 800 degrees Celsius during chemical vapor deposition. The continuous supply of oxygen increases the growth rate of graphene. They confirmed this by electron spectroscopy, but measurements showed that although oxygen was released, the total amount was small. The researchers explained that this may have a trapping effect on the very narrow space between the oxide substrate and the copper foil, thereby increasing the oxygen utilization efficiency. In the experiment, the researchers were able to produce 0.3 mm single crystal graphene in just 5 seconds.
The researchers said that this study is of great significance to the graphene industry. Through this technology, graphene production will enable a more efficient roll-to-roll process. The increase in production and cost reduction will further expand the use of graphene and stimulate its growth in demand. (Reporter Wang Xiaolong)
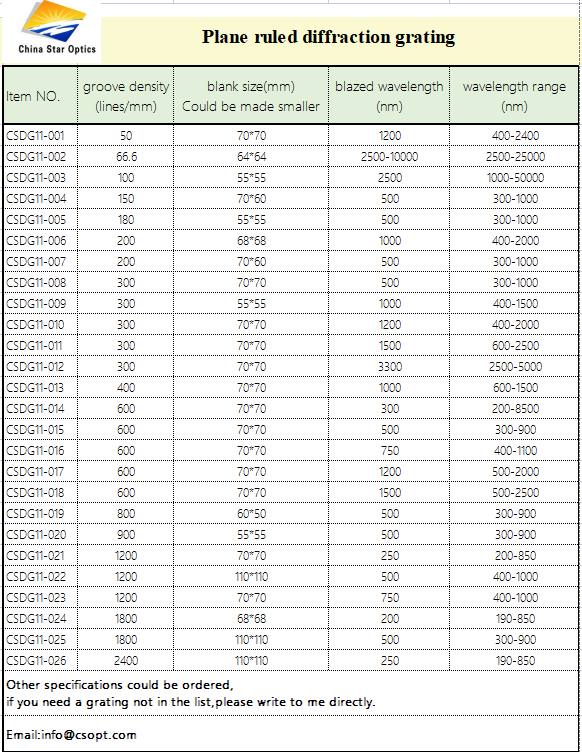
Plane ruled gratings are characterized by a superior efficiency at their design wavelength compared with holographic gratings. Plane Ruled gratings comprise the majority of diffraction gratings used in spectroscopic instrumentation and are especially useful in systems requiring high resolution.
China star optics can provide customers with a variety of replicated grating products such as diffraction gratings, reflective gratings,holographic gratings,concave gratings etc. to meet different needs. Maximum ruled area is up to 300 x 300 mm for plane ruled diffraction gratings. For replicated diffraction and transmission gratings the ruling density can be from 20 grooves per millimeter to 2400 grooves per millimeter, wavelength from 0.2 micron to 25 microns.
Holographic gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 0.2-0.8um
Grooves per mm: 1,200 to 3,600L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Ruled gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 0.2-15um
Grooves per mm: 50 to 2,400L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Concave gratings:
Specifications:
Ruled area: <=70 * 70mm
Wavelength range: 200 to 900um
Grooves per mm: 490 to 1,200L/mm
Diffraction: >70%
Plane Ruled Grating,Plane Ruled Diffraction Grating,Plane Reflection Grating,Plane Ruled Reflective Grating
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)