A transition zone of approximately 15.
Bolt fracture morphology 1.2 Crack position and state shows that the fracture is located between the tooth 1 and the tooth 2, and is concentrated on the tooth root of the tooth 1 . As can be seen from the assembly drawing, the 3rd to 6th thread is located at the counterbore of the fitting, and the 2nd thread is the first thread that cooperates with the internal thread of the fitting, that is, the fracture is beneficial to the initial joint of the bolt and the fitting.
Significant crack marks were observed in the roots (1st to 5th thread) of the four pitches. (a shows a low-power SEM image of the root crack of the 1st to 2nd threads, and the crack at the root is visible in the part indicated by the arrow. The metallographic phase shows cracks at the root of the 1st to 5th teeth. Depth 0. 15~0.30 No crack is found in the root arc of the 5th to 6th teeth. (b) is an enlarged view of the crack at the root of the 3rd to 4th tooth root. The angle of the bolt is about 59.6. The microstructure of the tooth root transition arc radius is about 0.32mm 2 , the microstructure and the hardness test are shown as the photomicrograph of the side edge of the thread. The base is a fine tempering state of tempered sorbite +3%. The dissolved iron body structure is normal, meeting the requirements of GB/T3098. 1-2000 to obtain more than 90% tempering sorbite; the edge color is obviously darker than other parts. Spectral chemical analysis is carried out on different depths of the bolt section (SFECTRCMEIER spectroscopy) The chemical composition of the instrument is shown in Table 1. It can be seen that the surface layer has been severely carburized. At the same time, according to GB/T3098.1-2000, the surface layer carburization is tested by the hardness method. The detection part is the tooth diameter measurement along the diameter line. The gradient values ​​are shown in Table 2. The test results show that the surface hardness is obvious.
Table 1 chemical composition analysis results (mass fraction, distance from the surface / mm heart table 2 hardness method surface carbon depth / mm 0.42 core adjacent tooth core hardness /. 3 defect analysis 3.1 F-zone analysis shown in the fracture analysis The section of the fatigue expansion zone, the section of the section and the axial direction of the bolt is about 90. The fatigue source is located at the location of the middle 1. The crack starts at the root of the thread. (a) shows the high-power SEM image of the fracture source of the F-zone, due to the source of the fracture crack. The part has been severely worn, its section is smooth, but there are still traces of micro-extrusion deformation and micro-cracks; (b) shows a low-magnification SEM image of the fracture edge of the F-zone, which has a characteristic of fatigue fracture. The shell line and the shell line have obvious propulsion marks. The shell line advances in an arc shape inward, and the line pattern is fine. In the middle and late stages, it is linearly pushed inward, and the line pattern is thicker. Rubbing makes the area brighter.
The S zone (instantaneous fault zone) shown in the section has a radioactive grain section, and the section of the section and the bolt axis is about 45 as a typical overload transient fracture morphology. For the high-power scanning electron microscope image of the fracture extension area (S-zone sampling), the micro-fracture feature is an equiaxed dimple, which is plastic fracture, and no non-metallic inclusions are seen in the dimple. It can be seen that the crack is mainly stretched and bent. Alternating stress.
The boundary between the fatigue section and the instantaneous section is obvious. It can be seen that the fracture is a sudden fracture caused by the overload stress at a certain moment after the fatigue cracking of the load surface.
3.2 Stress analysis As shown, there is no necking at the fracture site of the part, but there is a 4-tooth root ring crack near the fracture. After investigation, the bolt has an assembly torque of 750 Nm and is operated by a special torque wrench, which meets the requirements of the installation torque of 750 Nm.
From the analysis of the fracture part, the fracture is located at the initial joint of the bolt, that is, between the tooth 1 and the tooth 2 (see), the bolt is fixed by the thread glue during assembly, and the bolt is mainly subjected to the indicated moment, that is, During the bending load, the fulcrum should be at the initial joint of the thread, that is, the alternating load at the tooth groove between the tooth 1 and the tooth 2 is the most serious, that is, the stress concentration is the largest.
3 Dimensional analysis In order to improve the fatigue strength of the thread and reduce the sensitivity of the incision, for the high-strength external thread of class 8.8 or higher, the radius of the arc at the bottom of the tooth is required to be not less than 0.125P (where P is the pitch) (b), the bolt The radius of the thread bottom of the thread is about 0.32mm, which is close to the minimum allowable value of 0.313 (the bolt is a coarse thread of 10.9 grade 12.5). 3.4 Heat treatment analysis shows that the surface of the bolt thread has carburization phenomenon and is detected by chemical composition. The analysis confirmed that the thickness of the carburized layer was about 0.15 mm. The reason for carburization was that the carbon potential was improperly controlled during the atmosphere protection during the quenching and tempering process.
During the quenching process, the transformation temperature of the microstructure is related to the carbon content. The increase of the carbon content will lower the martensite transformation initiation temperature M. The surface carbonization causes the formation of martensite to lag behind the matrix, so the surface The phase change shrinkage is caused by the Martensitic system generated by the core, and the residual stress on the surface is expressed as tensile stress. Since the quenching hardness is related to the carbon content, the carbon content plus the quenching hardness will also increase, and at the same time, the surface plasticity decreases and the fatigue strength resistance is lowered.
4 Conclusions Based on the above analysis, the bolt fracture is caused by the occurrence of primary cracks in the root of the thread. The initial crack in the service is continuously expanded and propagated. When the crack expands to a certain depth, the stress of the section is sharply increased due to the reduction of the load-bearing area, resulting in sudden fracture. .
Because the bolt assembly torque meets the requirements of the specification, there is no obvious plastic deformation of the fracture, which can eliminate the primary crack caused by the assembly overload. Therefore, the main reason for the multiple cracks in the root is: severe carburization of the thread surface during the quenching and tempering process. The hardness and plasticity of the surface layer are decreased, and the surface layer stress is expressed as tensile stress, which increases the sensitivity of the surface layer crack. Secondly, because of the smaller radius of the root of the thread, the sensitivity of the root at the root is increased. Under the action of both, the fatigue resistance is reduced, and fatigue fracture occurs during service.
5 Improvement measures and effects The shape of the roller is modified to make the radius of the thread bottom of the thread increase reasonably, and the sensitivity of the cutting is strong. The heat treatment process controls the carbon potential reasonably, and periodically corrects the carbon potential to avoid surface carburization or decarburization; After the force shot blasting process can be strengthened, the compressive stress of the thread surface layer is generated, the fatigue strength of the thread is improved, the process control ability is strengthened, the physical and chemical detection is strengthened, and the surface de-osmosis of the thread is strictly checked according to the requirements of GB/T30981-2000 after heat treatment and quenching and tempering. Carbon and other mechanical and physical properties testing.
Based on the recommendations of the improvement measures, the manufacturer rectified the product, and the product has not experienced similar failures during its service.
The LED emergency inverter is a combination of a white high-quality ABS shell and an external lithium ion battery , which is small in size and easier to hide in the ceiling . This emergency conversion kit is suitable for all external driver of LED lights in the wide voltage AC85-265V range , equipped with lithium ion battery that can be recharged up to 500 times , the emergency power supply has multiple protection functions , such as overcharge , over-discharge , short circuit protection , etc .
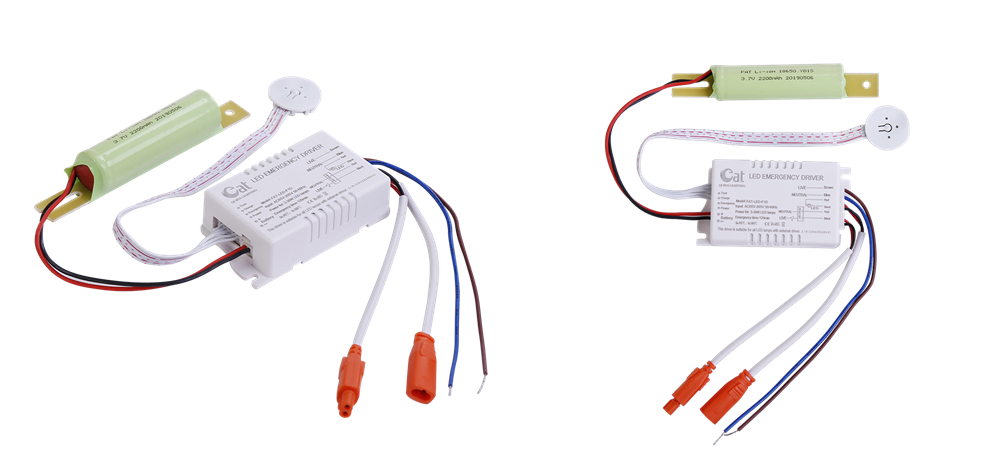
Led Inverter,Led Power Converter,Led Emergency Battery Driver,Emergency Light Conversion Kit
Jiangmen City Pengjiang District Qihui Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.qihuilights.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)